服务雪崩
-
在微服务架构中通常会有多个服务层调用,基础服务的故障可能会导致级联故障,进而造成整个系统不可用的情况,这种现象被称为服务雪崩效应
-
服务雪崩效应是一种因“服务提供者”的不可用导致“服务消费者”的不可用,并将不可用逐渐放大的过程
-
如果下图所示:A作为服务提供者,B为A的服务消费者,C和D是B的服务消费者。A不可用引起了B的不可用,并将不可用像滚雪球一样放大到C和D时,雪崩效应就形成了
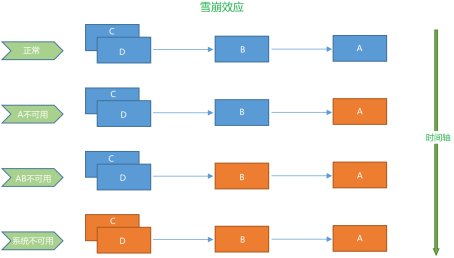
- 现实通常是更糟糕
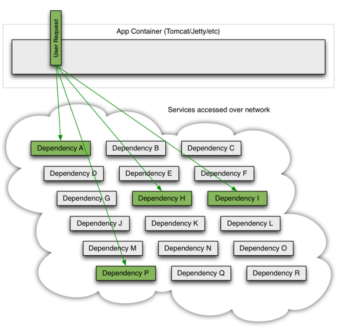
- 当一切正常时,请求看起来是这样的
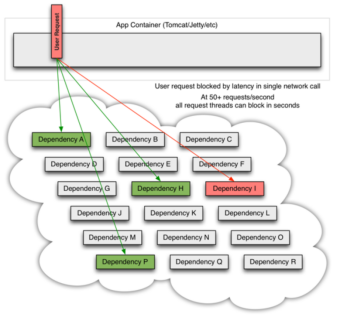
- 当其中有一个系统有延迟时,它可能阻塞整个用户请求
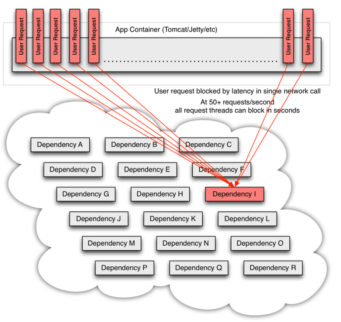
- 在高流量的情况下,一个后端依赖项的延迟可能导致所有服务器上的所有资源在数秒内饱和(PS:意味着后续再有请求将无法立即提供服务)
Hystrix

-
Hystrix是NetFlex公司提供的一套用于分布式系统的延迟和容错的开源库。在分布式系统里,许多依赖不可避免的调用失败,比如超时、异常等,Hystrix能够保证在一个依赖出问题的情况下,不会导致整个服务失败,避免级联故障,以提高分布式系统的弹性
-
Hystrix的作用:服务降级、服务熔断、服务限流
- 服务降级
- 为了保证“核心业务”一切正常,我们可能会让一些“非核心业务”不提供它的功能,让它服务降级,直接提醒用户:“服务器当前繁忙,请稍后再试”,不让客户端等待并立刻返回一个友好提示,fallback
- 哪些情况会触发降级的情况
- 程序运行异常(没有处理异常try-catch)、超时、服务熔断触发服务降级、线程池/信号量打满也会导致服务降级
- 服务熔断
- 类比保险丝达到最大服务访问后,直接拒绝访问,拉闸限电,然后调用服务降级的方法并返回友好提示,就是保险丝:服务的降级 -> 进而熔断 -> 恢复调用链路
- 服务限流
- 秒杀高并发等操作,严禁一窝蜂的过来拥挤, 大家排队,一秒钟N个,有序进行
- 服务降级
-
一般来讲:先配置服务限流,然后再配置服务降级,进而服务熔断
-
目的:都是为了保证在高并发的情况,系统永远是可用的
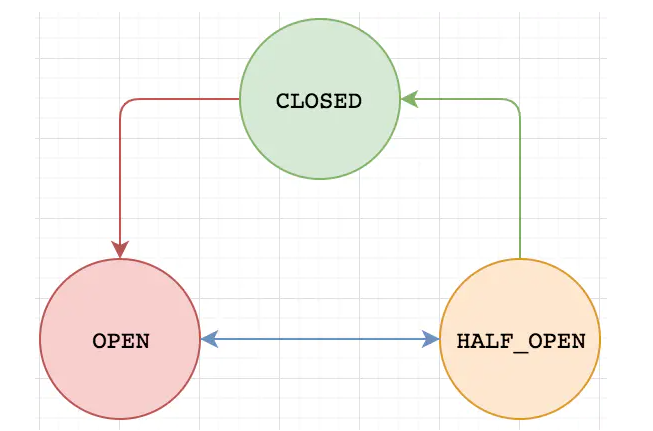
熔断器的3个状态
-
Closed
- 关闭状态(断路器关闭),所有请求都正常访问。代理类维护了最近调用失败的次数,如果某次调用失败,则使失败次数加1。如果最近失败次数超过了在给定时间内允许失败的阈值,则代理类切换到断开(Open)状态。此时代理开启了一个超时时钟,当该时钟超过了该时间,则切换到半断开(Half-Open)状态。该超时时间的设定是给了系统一次机会来修正导致调用失败的错误
-
OPEN
- 打开状态(断路器打开),所有请求都会被降级。Hystix会对请求情况计数,当一定时间内失败请求百分比达到阈值,则触发熔断,断路器会打开。默认失败比例的阈值是50%,请求次数最少不低于20次,默认是10S
-
Half Open
- 半开状态,open状态不是永久的,打开后会进入休眠时间(默认是5S)。随后断路器会自动进入半开状态。此时会释放1次请求通过,若这个请求是健康的,则会关闭断路器,否则继续保持OPEN状态,再次进行5秒休眠计时
Hystrix使用
RestTemplate和Hystrix整合
1、添加依赖
<!-- 导入熔断器的启动器 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-netflix-hystrix</artifactId>
</dependency>
2、服务消费者启动类上,添加注解@EnableCircuitBreaker开启熔断器
@SpringBootApplication
@EnableEurekaClient
@EnableCircuitBreaker
public class OrdersApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(OrdersApplication.class,args);
}
@Bean
@LoadBalanced
public RestTemplate getRestTemplate(){
return new RestTemplate();
}
}
3、在消费者控制层调用RestTemplate方法上(也可以是提供者被调用方法上添加),添加注解@HystrixCommand,并声明熔断降级备选方法
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/orders")
public class OrdersController {
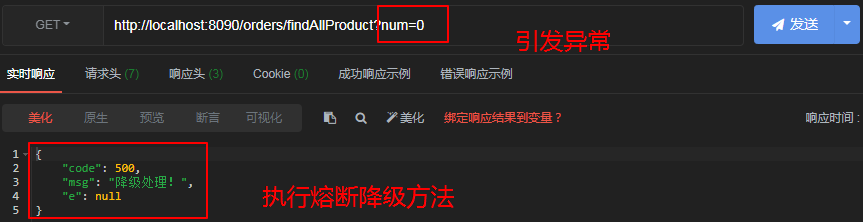
//如果该方法或服务提供者发生异常,那么会执行熔断降级方法
@HystrixCommand(defaultFallback = "errorResult")
@GetMapping("/findAllProduct")
public ResultVO findAllProduct(Integer num){
System.out.println(1 / num);
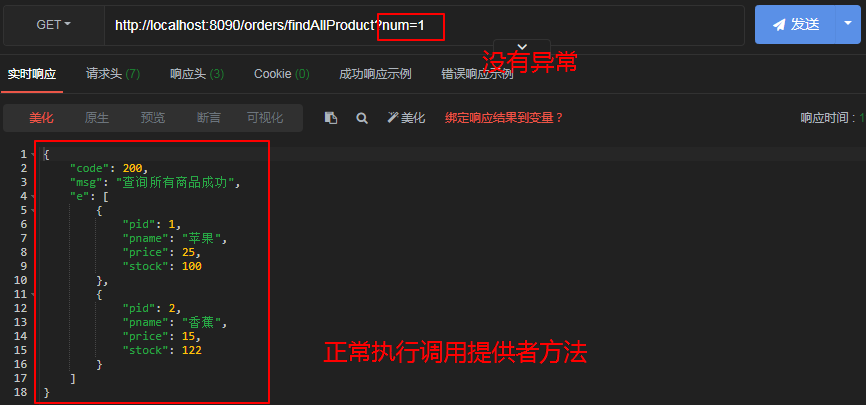
ResultVO resultVO = restTemplate.getForObject("http://star-product/product/findAllProduct",ResultVO.class);
return resultVO;
}
//熔断降级方法
public ResultVO errorResult(){
return ResultVO.fail("降级处理!");
}
}
4、观察效果
OpenFeign和Hystrix整合(常用)
使用前提
项目中需要导入feign依赖,以及在启动类上开启feign,不需要额外导入Hystrix依赖,因为OpenFeign自带
1、消费者配置文件中打开feign中的hystrix,默认没有打开
feign:
hystrix:
enabled: true
2、服务消费者启动类上,添加注解@EnableCircuitBreaker开启熔断器
@SpringBootApplication
@EnableEurekaClient
@EnableFeignClients
@EnableCircuitBreaker
public class OrdersApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(OrdersApplication.class,args);
}
}
3、声明feign接口,以及调用的提供者方法,注解声明降级处理类
//fallback声明了用于降级处理类
@FeignClient(value = "star-product",fallback = ProductServerFeignImpl.class)
public interface ProductServerFeign {
@GetMapping("/product/findAllByNum/{num}")
ResultVO findAllByNum(@PathVariable("num") Integer num);
}
4、在feign客户端(接口)的实现类声明降级的处理,并被spring容器管理
该类中重写的方法,即为对应feign接口中方法在运行出现熔断降级时,执行的方法
//需要被spring容器管理
@Component
public class ProductServerFeignImpl implements ProductServerFeign {
public ResultVO findAllByNum(Integer num) {
return ResultVO.fail("触发降级处理!");
}
}
5、测试
5.1、提供者控制层
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/product")
public class ProductController {
@Autowired
private ProductService productService;
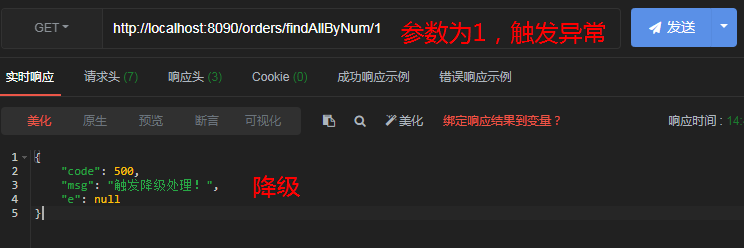
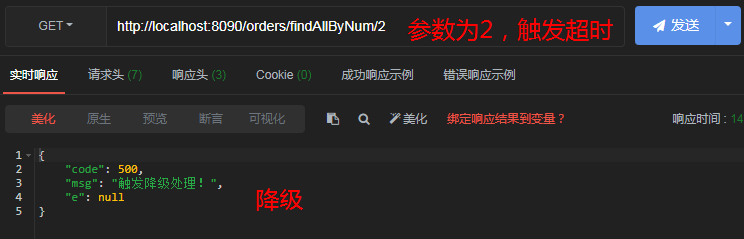
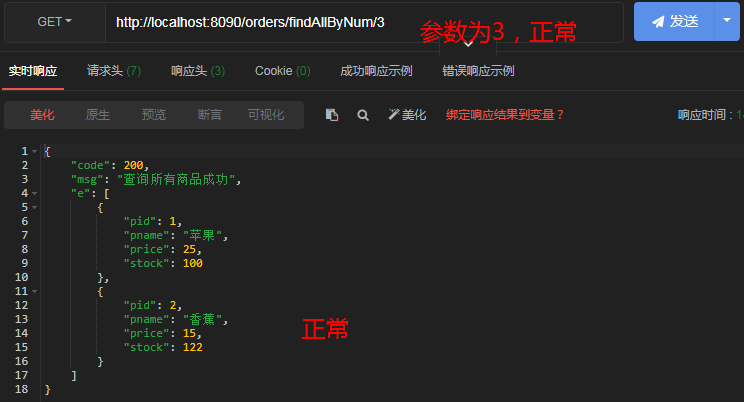
//如果参数为1,则引发异常;如果参数为2,则引发超时
@GetMapping("/findAllByNum/{num}")
public ResultVO findAllByNum(@PathVariable("num") Integer num) throws InterruptedException {
if(num == 1){
System.out.println(1/0);
}
if(num == 2){
Thread.sleep(2000);
}
List<Product> list = productService.findAllProduct();
return ResultVO.success("查询所有商品成功",list);
}
}
Hystrix配置
全局配置
在消费者的application.yml中,进行配置
避坑1:此时的timeoutInMilliseconds需要大于ribbon的默认读取时间(1秒)和默认连接时间(1秒),否则,ribbon没有来得及重试,就会熔断
避坑2:如果程序的读取速度过慢,例如,自己手动设置线程睡眠超过1秒,就需要修改ribbon的默认读取时间
hystrix:
command:
default:
circuitBreaker:
requestVolumeThreshold: 20 #10S范围内,熔断器至少接收20个请求,才会执行熔断判断逻辑,默认20个
sleepWindowInMilliseconds: 5000 #熔断以后,5S内,熔断器的状态都出于半开状态,默认5秒
errorThresholdPercentage: 50 #10S范围内,超过50%的请求出问题,服务开始熔断,默认50%
execution:
isolation:
thread:
timeoutInMilliseconds: 1000 #超过1秒钟,微服务调用将超时,默认1秒
局部配置
注解配置
@HystrixCommand(fallbackMethod="fallback",
commandProperties = {
@HystrixProperty(name = "execution.isolation.thread.timeoutInMilliseconds", value = "1000" )
}
)
针对服务配置
针对服务级别的话,直接配置service-id,如下:
hystrix:
command:
service-id:
execution:
isolation:
thread:
timeoutInMilliseconds: 3000
Hystrix DashBoard
- 微服务配置了Hystrix熔断规则,Hystrix-DashBoard可以帮我们分析熔断的情况
- 该技术,主要用来帮助项目经理,统计/分析熔断数据
创建DashBoard的微服务
1、导入依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-actuator</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-netflix-hystrix-dashboard</artifactId>
</dependency>
2、编写application.yml配置文件
server:
port: 7070
spring:
application:
name: hystrix-dashBoard
3、编写启动类,添加注解
@SpringBootApplication
@EnableHystrixDashboard
public class DashBoardApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(DashBoardApplication.class,args);
}
}
4、启动,访问
DashBoard监控微服务
如果是OpenFeign和Hystrix整合,没有加入Hystrix依赖的话,那么需要在该微服务上,添加依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-netflix-hystrix</artifactId>
</dependency>
并且在该项目的启动类上,添加@EnableCircuitBreaker
1、在需要监控的微服务中,添加依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-actuator</artifactId>
</dependency>
2、修改启动类,添加Servlet的支持
- Spring Cloud使用G及其之前的版本不用写配置类,升级到H以后还有写个配置信息
- 在启动类添加下面的代码
/**
* 此配置是为了服务监控而配置,与服务器容器本身无关,springcloud升级后的坑
* ServletRegistrationBean因为springboot的默认路径不是/hystrix.stream
* 只要在自己的项目里配置下面的servlet就可以了
*/
@Bean
public ServletRegistrationBean getServlet() {
HystrixMetricsStreamServlet streamServlet = new HystrixMetricsStreamServlet();
ServletRegistrationBean registrationBean = new ServletRegistrationBean(streamServlet);
registrationBean.setLoadOnStartup(1);
registrationBean.addUrlMappings("/hystrix.stream");
registrationBean.setName("HystrixMetricsStreamServlet");
return registrationBean;
}
3、在DashBoard微服务的application.yml中,添加配置
hystrix:
dashboard:
proxy-stream-allow-list: "localhost"
4、使用
例如:http://localhost:8090/hystrix.stream
可以查看出,在被监控微服务调用时,在向dashboard发送消息
测试效果

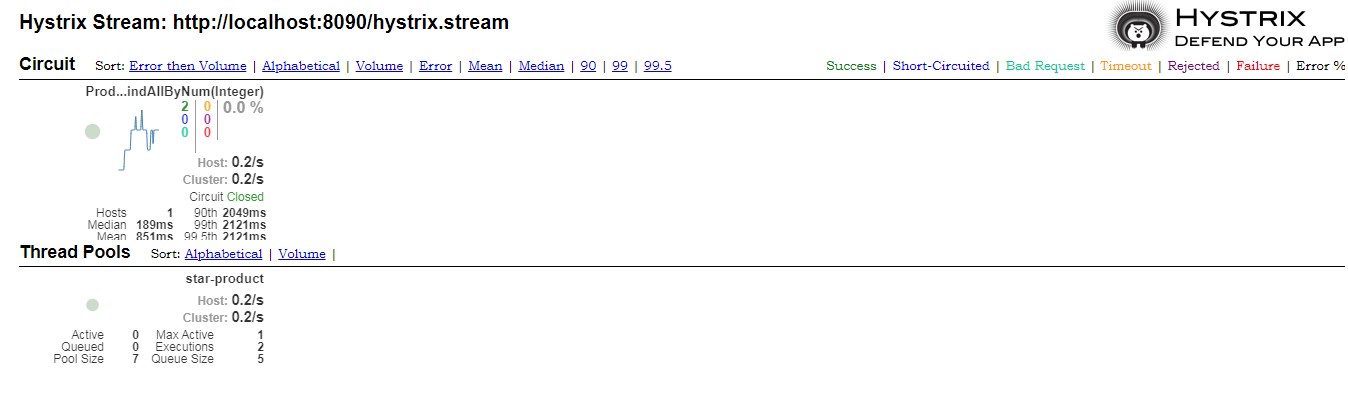
监控中各项图标的意义
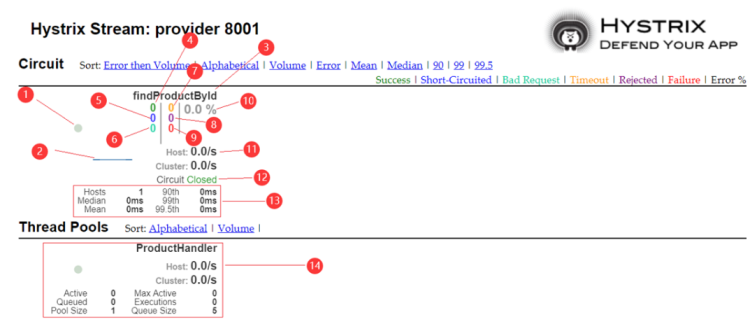
| 编号 | 解释 |
|---|---|
| 1 | 圆点:微服务的健康状态,有绿色,黄色,橙色,红色,健康状态依次降低 |
| 2 | 线条:流量变化 |
| 3 | 请求的方法 |
| 4 | 成功请求(绿色) |
| 5 | 短路请求(蓝色) |
| 6 | 坏请求(青色) |
| 7 | 超时请求(黄色) |
| 8 | 被拒绝的请求(紫色) |
| 9 | 失败请求(红色) |
| 10 | 最近10秒钟内请求错误的百分比 |
| 11 | 请求频率 |
| 12 | 熔断器状态 |
| 13 | 数据延迟统计 |
| 14 | 线程池 |
Sentinel(Alibaba)
客户端弹性模式
客户端弹性模式的重点是,当远程服务表现不佳或发生错误的时候,保护调用该远程服务的客户端,让该客户端能够“快速失败”,而不消耗诸如数据库连接和线程池之类的宝贵资源,从而避免客户端崩溃。常见的客户端弹性模式有:隔离、超时、限流、熔断、降级。
- 隔离
- 将系统按照一定的原则划分为若干个服务模块,各个模块之间相对独立。当有故障发生时,能将问题隔离在某个模块内部,而不扩散风险,不波及其他模块,不影响整体的系统服务。常见的隔离方式有:线程池隔离。
- 超时
- 在上游服务调用下游服务的时候,设置一个最大响应时间,如果调用远程服务所花费的时间超过这个时间,就断开请求,释放掉线程。
- 限流QOS
- 限流就是限制系统的输入和输出流量,以达到保护系统的目的。为了保证系统的稳定运行,一旦达到需要限制的阈值,就需要限制流量。
- 熔断
- 在互联网系统中,当下游服务因访问压力过大而导致响应变慢或失败时,上游服务为了保护整体系统的可用性,可以暂时切断对下游服务的调用。这种局部牺牲,保全整体的措施就叫做熔断。
- 降级
- 降级就是为服务提供一个后备方案,一旦下游服务无法正常调用,就是用后备方案
Sentinel安装与配置
1、下载并运行sentinel
1.1、下载
https://github.com/alibaba/Sentinel/releases
1.2、运行
把sentinel拷贝项目同级目录,在cmd中运行sentinel项目
账号密码默认为sentinel
java -Dserver.port=9090 -Dcsp.sentinel.dashboard.server=localhost:9090 -Dproject.name=sentinel-dashboard -jar sentinel-dashboard-1.7.1.jar
2、服务添加依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-alibaba-sentinel</artifactId>
</dependency>
3、修改服务配置文件
spring:
cloud:
sentinel:
transport:
port: 9999 # 与控制台交流的端口,随意指定一个未使用的端口即可
dashboard: localhost:9090 # 指定控制台服务的地址
4、启动nacos、被监听的服务、sentinel控制台
通过localhost:9090访问sentinel控制台
需要访问上游服务的控制层方法,才可以在sentinel控制台中显示

Sentinel应用
一、流量控制
1、QPS每秒访问数
可以控制指定资源路径的每秒访问数
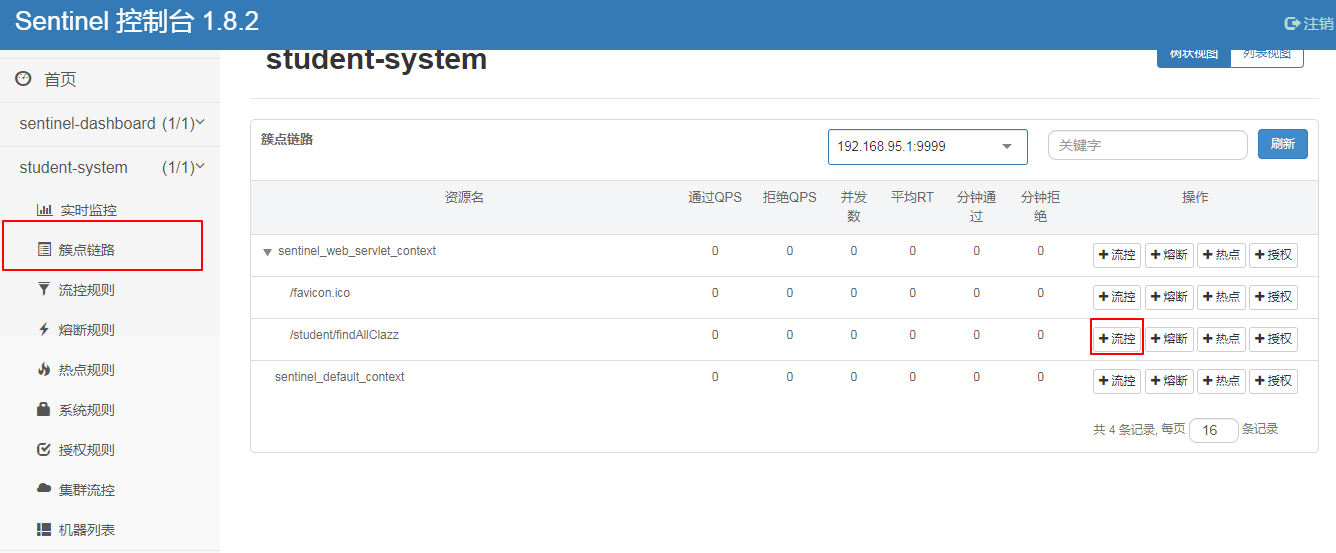
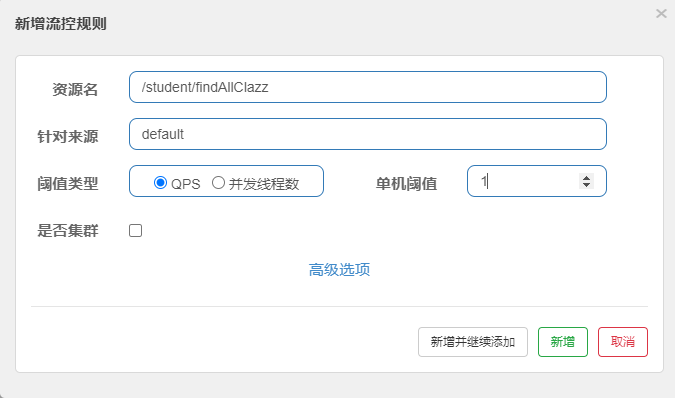
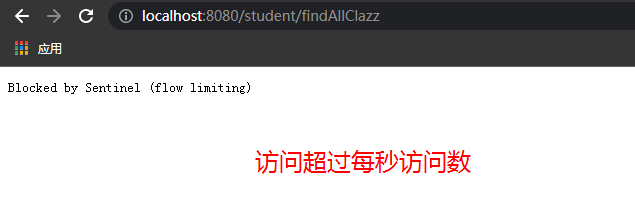
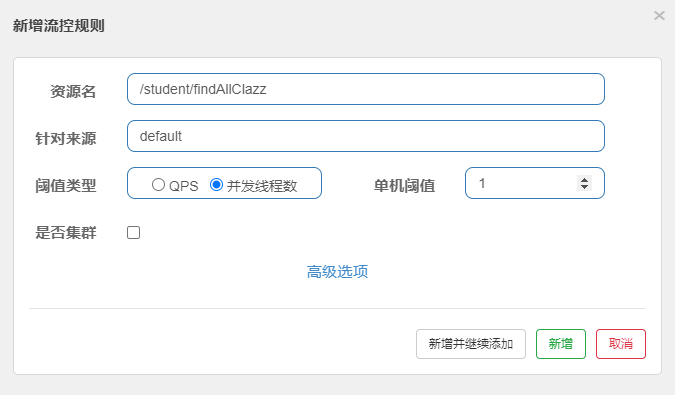
2、线程
可以控制指定资源路径的并发线程数
3、流控的模式
-
直接:对接口的访问达到限流条件时,开启限流。(默认值)
-
关联:当关联的资源达到限流条件时,开启限流。
- 例如,在资源路径test1中设置关联test2,如果test2没有超过自身的阈值,那么test1可以一直访问,但是,如果test2超过了自身的阈值,那么test1无法访问
-
链路:当从某个接口过来的资源达到限流条件时,开启限流。
-
对于同一service资源,被控制层的两个方法调用时,可以通过在该service方法上添加@SentinelResource("资源名称")的注解,并且,在簇点链路中设置该资源流控为链路,来控制该资源限流
-
链路流控时需要添加配置和代码
-
spring: application: name: star-orders cloud: nacos: config: server-addr: localhost:8848 file-extension: yml sentinel: transport: port: 9999 # 与控制台交流的端口,随意指定一个未使用的端口即可 dashboard: localhost:8080 # 指定控制台服务的地址 filter: enabled: false # 关闭sentinel的CommonFilter实例化 -
@Configuration public class RootConfig { @Bean public FilterRegistrationBean sentinelFilterRegistration() { FilterRegistrationBean registration = new FilterRegistrationBean(); registration.setFilter(new CommonFilter()); registration.addUrlPatterns("/*"); // 入口资源关闭聚合 registration.addInitParameter(CommonFilter.WEB_CONTEXT_UNIFY, "false"); registration.setName("sentinelFilter"); registration.setOrder(1); return registration; } }
-
-
4、流控效果
- 快速失败:直接失败,抛出异常,不做任何额外的处理,是最简单的效果
- Warm up: Warm Up(RuleConstant.CONTROL_BEHAVIOR_WARM_UP)方式,即预热/冷启动方式。当系统长期处于低水位的情况下,当流量突然增加时,直接把系统拉升到高水位可能瞬间把系统压垮。通过"冷启动",让通过的流量缓慢增加,在一定时间内逐渐增加到阈值上限,给冷系统一个预热的时间,避免冷系统被压垮。
- 排队等待:让请求以均匀的速度通过,单机阈值为每秒通过数量,其余的排队等待;它同时还允许设置一个超时时间,当请求超过超时时间还未处理时,则丢弃该请求。
二、降级规则
1、超时进行降级
访问超时,会进行降级
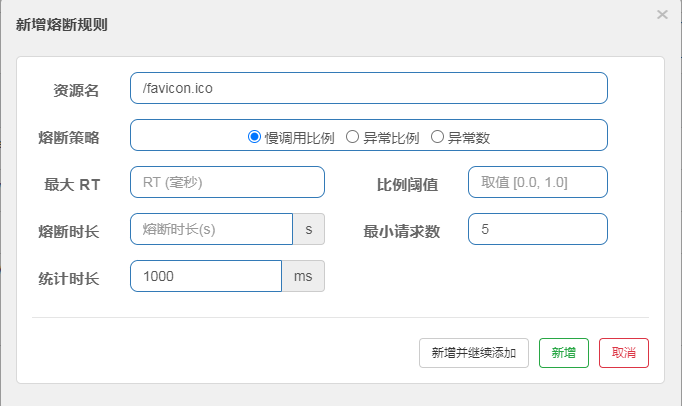
2、异常比例
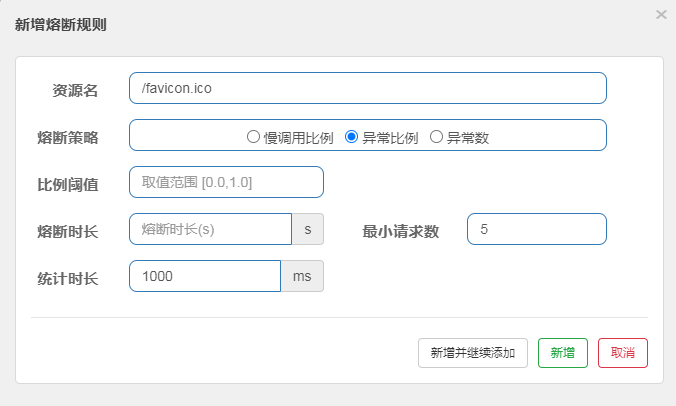
3、异常数
在一定时间内,异常数量到达阈值则进行降级
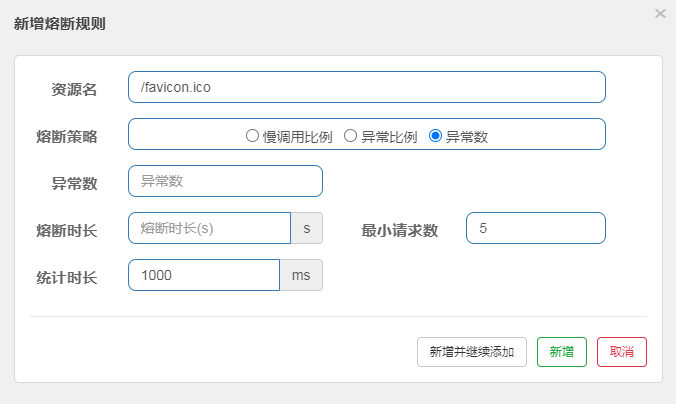
三、热点规则
热点规则可以对控制层的参数进行流量控制,如果该参数达到阈值,就会进行熔断
1、参数访问流量的控制
在需要添加热点规则的控制层方法上添加注解添加@SentinelResource("资源名称")
对该资源进行添加热点规则
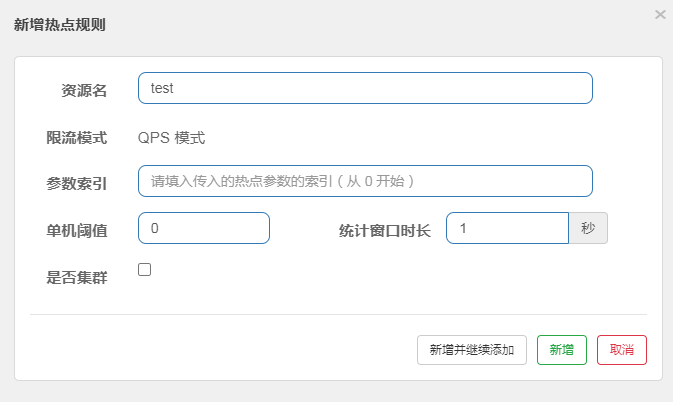
2、特定参数值访问流量的控制排除
在热点控制规则生成后,进行编辑,编辑例外的参数值
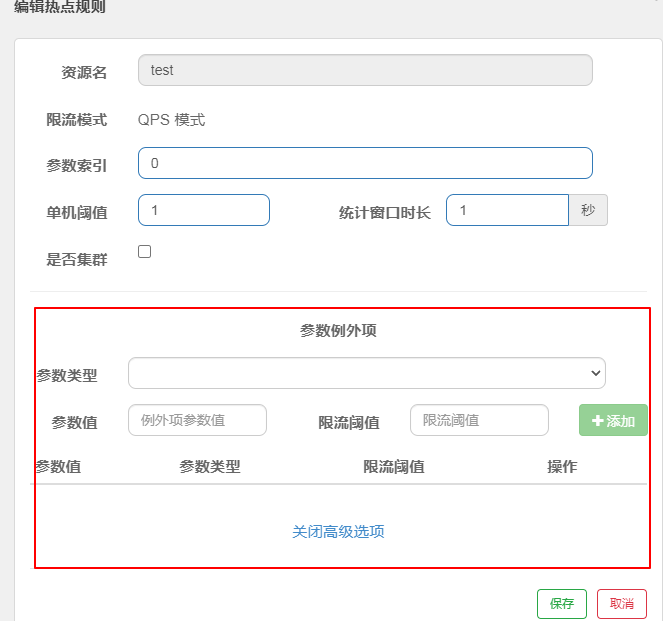
四、授权规则
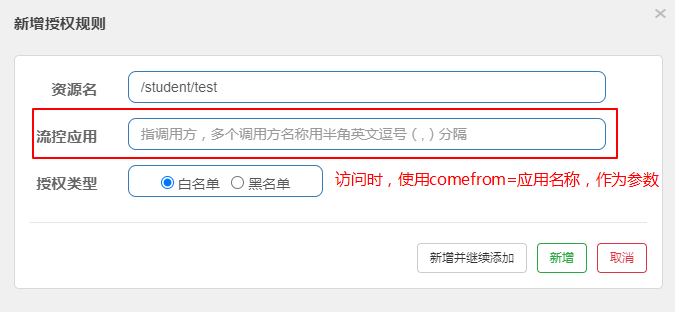
很多时候,我们需要根据调用来源来判断该次请求是否允许放行,这时候可以使用 Sentinel 的来源访问控制的功能。来源访问控制根据资源的请求来源(origin)限制资源是否通过:
- 若配置白名单,则只有请求来源位于白名单内时才可通过
- 若配置黑名单,则请求来源位于黑名单时不通过,其余的请求通过
- 此规则需要自定义来源名称
1、在微服务中添加自定义来源处理规则
@Component
public class MyRequestOriginParser implements RequestOriginParser {
@Override
public String parseOrigin(HttpServletRequest httpServletRequest) {
String comefrom = httpServletRequest.getParameter("comefrom");
return comefrom;
}
}
2、对资源路径进行授权规则的设置
五、系统规则
系统保护规则是从应用级别的入口流量进行控制,从单台机器的总体 Load、RT(平均响应时间)、入口 QPS 、CPU使用率和线程数五个维度监控应用数据,让系统尽可能保持在最大吞吐量的情况下,还能保证系统整体的稳定性。
系统保护规则是应用整体维度的,而不是资源维度的,并且仅对入口流量 (进入应用的流量) 生效。
-
Load(仅对 Linux/Unix-like 机器生效):当系统 load1 (load1指1分钟之内的平均负责)超过阈值,且系统当前的并发线程数超过系统容量时才会触发系统保护。系统容量由系统的 maxQps * minRt 计算得出。设定参考值一般是 CPU cores * 2.5。
-
RT:当单台机器上所有入口流量的平均 RT 达到阈值即触发系统保护,单位是毫秒。
-
线程数:当单台机器上所有入口流量的并发线程数达到阈值即触发系统保护。
-
入口 QPS:当单台机器上所有入口流量的 QPS 达到阈值即触发系统保护。
-
CPU使用率:当单台机器上所有入口流量的 CPU使用率达到阈值即触发系统保护。
六、规则触发后,设置统一显示结果
以下的类,会自动拦截所有Sentinel为了保护资源而抛出的异常,我们可以根据异常的具体类型,来向客户端响应具体的信息
@Component
public class MyUrlBlockHandler implements UrlBlockHandler {
@Override
public void blocked(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, BlockException e) throws IOException {
response.setContentType("application/json;charset=utf-8");
ResultVO r = null;
//BlockException 异常接口,包含Sentinel的五个异常
//1、 FlowException 限流异常
//2、 DegradeException 降级异常
//3、 ParamFlowException 参数限流异常
//4、 AuthorityException 授权异常
//5、 SystemBlockException 系统负载异常
if (e instanceof FlowException) {
r = new ResultVO(-1, "接口被限流了...");
} else if (e instanceof DegradeException) {
r = new ResultVO(-2, "接口被降级了...");
}
response.getWriter().write(JSON.toJSONString(r));
}
}
对于使用注解@SentinelResource声明的资源,可以使用自定义方法进行处理
//blockHandler声明的方法需要有参数为BlockException,用于接收抛出的规则的异常
//fallbackHandler,用于其他异常
@SentinelResource(value = "test",blockHandler = "paramFlowHadler",fallback = "fallbackHandler")
七、规则持久化
sentinel中每次重启服务时,对应服务的规则都需要重新配置,一旦项目进入生产环境,规则变动不大,而且配置会有很多,这时就要使用规则持久化。
1、编写一个持久化工具类
public class FilePersistence implements InitFunc {
@Override
public void init() throws Exception {
// TIPS: 如果你对这个路径不喜欢,可修改为你喜欢的路径
String ruleDir = System.getProperty("user.home") + "/sentinel/rules";
System.out.println(ruleDir);
String flowRulePath = ruleDir + "/flow-rule.json";
String degradeRulePath = ruleDir + "/degrade-rule.json";
String systemRulePath = ruleDir + "/system-rule.json";
String authorityRulePath = ruleDir + "/authority-rule.json";
String paramFlowRulePath = ruleDir + "/param-flow-rule.json";
this.mkdirIfNotExits(ruleDir);
this.createFileIfNotExits(flowRulePath);
this.createFileIfNotExits(degradeRulePath);
this.createFileIfNotExits(systemRulePath);
this.createFileIfNotExits(authorityRulePath);
this.createFileIfNotExits(paramFlowRulePath);
// 流控规则
ReadableDataSource<String, List<FlowRule>> flowRuleRDS = new FileRefreshableDataSource<>(
flowRulePath,
flowRuleListParser
);
// 将可读数据源注册至FlowRuleManager
// 这样当规则文件发生变化时,就会更新规则到内存
FlowRuleManager.register2Property(flowRuleRDS.getProperty());
WritableDataSource<List<FlowRule>> flowRuleWDS = new FileWritableDataSource<>(
flowRulePath,
this::encodeJson
);
// 将可写数据源注册至transport模块的WritableDataSourceRegistry中
// 这样收到控制台推送的规则时,Sentinel会先更新到内存,然后将规则写入到文件中
WritableDataSourceRegistry.registerFlowDataSource(flowRuleWDS);
// 降级规则
ReadableDataSource<String, List<DegradeRule>> degradeRuleRDS = new FileRefreshableDataSource<>(
degradeRulePath,
degradeRuleListParser
);
DegradeRuleManager.register2Property(degradeRuleRDS.getProperty());
WritableDataSource<List<DegradeRule>> degradeRuleWDS = new FileWritableDataSource<>(
degradeRulePath,
this::encodeJson
);
WritableDataSourceRegistry.registerDegradeDataSource(degradeRuleWDS);
// 系统规则
ReadableDataSource<String, List<SystemRule>> systemRuleRDS = new FileRefreshableDataSource<>(
systemRulePath,
systemRuleListParser
);
SystemRuleManager.register2Property(systemRuleRDS.getProperty());
WritableDataSource<List<SystemRule>> systemRuleWDS = new FileWritableDataSource<>(
systemRulePath,
this::encodeJson
);
WritableDataSourceRegistry.registerSystemDataSource(systemRuleWDS);
// 授权规则
ReadableDataSource<String, List<AuthorityRule>> authorityRuleRDS = new FileRefreshableDataSource<>(
authorityRulePath,
authorityRuleListParser
);
AuthorityRuleManager.register2Property(authorityRuleRDS.getProperty());
WritableDataSource<List<AuthorityRule>> authorityRuleWDS = new FileWritableDataSource<>(
authorityRulePath,
this::encodeJson
);
WritableDataSourceRegistry.registerAuthorityDataSource(authorityRuleWDS);
// 热点参数规则
ReadableDataSource<String, List<ParamFlowRule>> paramFlowRuleRDS = new FileRefreshableDataSource<>(
paramFlowRulePath,
paramFlowRuleListParser
);
ParamFlowRuleManager.register2Property(paramFlowRuleRDS.getProperty());
WritableDataSource<List<ParamFlowRule>> paramFlowRuleWDS = new FileWritableDataSource<>(
paramFlowRulePath,
this::encodeJson
);
ModifyParamFlowRulesCommandHandler.setWritableDataSource(paramFlowRuleWDS);
}
private Converter<String, List<FlowRule>> flowRuleListParser = source -> JSON.parseObject(
source,
new TypeReference<List<FlowRule>>() {
}
);
private Converter<String, List<DegradeRule>> degradeRuleListParser = source -> JSON.parseObject(
source,
new TypeReference<List<DegradeRule>>() {
}
);
private Converter<String, List<SystemRule>> systemRuleListParser = source -> JSON.parseObject(
source,
new TypeReference<List<SystemRule>>() {
}
);
private Converter<String, List<AuthorityRule>> authorityRuleListParser = source -> JSON.parseObject(
source,
new TypeReference<List<AuthorityRule>>() {
}
);
private Converter<String, List<ParamFlowRule>> paramFlowRuleListParser = source -> JSON.parseObject(
source,
new TypeReference<List<ParamFlowRule>>() {
}
);
private void mkdirIfNotExits(String filePath) throws IOException {
File file = new File(filePath);
if (!file.exists()) {
file.mkdirs();
}
}
private void createFileIfNotExits(String filePath) throws IOException {
File file = new File(filePath);
if (!file.exists()) {
file.createNewFile();
}
}
private <T> String encodeJson(T t) {
return JSON.toJSONString(t);
}
}
2、在配置目录新建一个文件
在resouces下创建META-INF/services目录
并在该目录下新建文件,文件名为com.alibaba.csp.sentinel.init.InitFunc,
文件内容为配置类的全类名top.ygang.config.FilePersistence
八、Feign和sentinel的组合
1、添加依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-alibaba-sentinel</artifactId>
</dependency>
2、yml配置激活feign和sentinel组合
feign:
sentinel:
enabled: true
3、编写fallback类
有两种,分别fallback和fallbackFactory,两种都可以实现
fallback
//自定义类实现feign接口
@Service
public class ProductFallback implements IProductService {
@Override
public ResultVO findAllProduct() {
return ResultVO.success("使用ProductFallback的备用方法");
}
}
对应的feign接口中需要添加注解信息
@FeignClient(
value = "star-product",
fallback = ProductFallback.class
)
fallbackfactory
//自定义类实现FallbackFactory接口,泛型为feign接口
@Service
public class ProductFallbackFactory implements FallbackFactory<IProductService> {
@Override
public IProductService create(Throwable throwable) {
System.out.println("ProductFallbackFactory.create:"+throwable);
return new IProductService() {
@Override
public ResultVO findAllProduct() {
return ResultVO.success("这是ProductFallbackFactory中的备用方法!!");
}
};
}
}
对应的feign接口中需要添加注解信息
@FeignClient(
value = "star-product",
fallbackFactory = ProductFallbackFactory.class
)